COMPUTER SYSTEM
1.1 INTRODUCTION OF COMPUTER
• The word ‘Computer ‘is derived from the Latin word ‘Computare’.
• An electronic device that can perform any kind of work involving arithmetic and logical
operations on data.
• A fast and accurate electronic programmable device that accepts data and instructions, processes them as the instructions, and produces information as an output.
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTER
• Speed: process tasks at high speed.
• Accuracy: 100% accurate if there is no GIGO and bugs.
• Automatic: No need to instruct once the instructions are fed.
• Storage: Stores data in the form of binary digits and can has a huge storage capacity.
• Diligence: Capable of performing tasks repeatedly without losing efficiency.
• Versatility: Capability of doing various kinds of tasks
• Reliability
• No Intelligence: cannot take its own decision
• No Feeling
APPLICATION
OF COMPUTERS
• OFFICE
• BANKING
• BUSINESS
• E-GOVERNANCE
• COMMUNICATION
• TRANSPORTATION
• EDUCATION
• INDURSTRY
• HEALTH
• ENTERTAINMENT
APPLICATION OF COMPUTERS
· OFFICE
– To prepare, store and retrieve data as electronic files.
– To handle correspondence and office communications.
– To facilitate administrative work and prepare papers.
– To assist in decision making.
· BANKING
– To control the entire baking system.
– To maintain customers’ accounts. Computers help to calculate payments, interest, and balance of customers.
– To provide online banking services like internet banking, money transferring, SMS (Short Message Service) banking, mobile banking, ABBS (Any Branch Banking Service), etc. to customers.
– To provide electronic banking services like Automated Teller Machine (ATM).
– To supervise the entire banking activities.
·
BUSINESS
– To manage financial transaction,
– To provide Security,
– To manage stock,
– To boost e-commerce.
– To boost the business by creating websites, ads, etc.,
– To provide communication facilities like email and instant messaging,
– To create documents and reports,
– To give information and provide training to employees.
· E-GOVERNANCE
– To facilitate access to government information, services, and products.
– To promote civic engagement by allowing citizens to interact with government officials.
– To make the government more accountable by making its operations more transparent and thus reducing the opportunities for corruption.
– To provide opportunities for development, particularly to rural and traditionally underserved communities.
– To establish a paperless working system.
– To increase public participation in the policy and decision-making processes of government.
·
COMMUNICATION
– To do fast and economic communication.
– To communicate among people at different locations.
·
TRANSPORTATION
– To controlling traffics
– To provide information and reservation facilities to people.
– To track vehicles
– To guiding drivers.
EDUCATION
– To increase access to education.
– To improve the quality of teaching and learning.
– To improve knowledge sharing.
– To increase the efficiency and effectiveness in administration and classrooms.
– To prepare notes, reports, and presentations of lectures.
– To facilitate distance learning education.
– To conduct online examinations.
· INDURSTRY
– controlling the quality of products,
– controlling/operating heavy machines and tools,
– performing dangerous tasks.
– detecting specific errors or defects that occurred in the process.
·
HEALTH
– To assist doctors
– To monitor the condition of patients
– To record the necessary information of patients
– To diagnose diseases in patients.
·
ENTERTAINMENT
– To entertain people of all ages.
– To compose music and set tunes.
– To put special effects in movies.
– To edit songs and movies.
1.1.2 EVOLUTION OF COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY
Harvard Mark-I (1937-1944)
·
1st
electromechanical computer developed in the leadership of Howard Aiken with IBM
engineers.
·
Named as
IBM Automatic Sequence Controlled Computer (ASCC).
·
Consists of
mechanical switches and could perform arithmetic operations.
·
as well as
solve more complex equations.
·
8 feet
high, 51 feet long and 2 feet wide and weighed 35 tons.
Atanasoff
Berry Computer (ABC)
·
Developed
by John Vincent Atanasoff and Clifford Berry in 1937-1942
·
1st
workable machine that had used binary number system.
·
Could solve
29 simultaneous equations.
• Z3
computer
·
Electro-mechanical
computer designed by Knorad Zuse in 1941 AD
·
Fully
automatic first working programmable computing machine.
Electronic Computers Era
• Based on electron tubes/vacuum tubes or valves, and transistors.
• ENIAC, EDVAC, EDSAC, UNIVAC, ENIAC
First
Generation Computers (1943-1958)
• Vacuum
tube as the main electronic component.
• Magnetic
drum as primary storage.
• Punched
cards and paper tape as input and output devices.
• Magnetic
tape as secondary memory.
• Large but
slow in operation and could perform tasks in milliseconds.
• Consume a
very high amount of electricity and produced too much heat.
• No OS and
had to setup manually.
•
Programmed in machine language.
Vacuum Tube
• Developed
by John Ambrose Fleming in 1904 AD
• More
improved vacuum tube was developed by Lee De Forest in 1906 AD.
• Used as a
switch or an amplifier in the early computers.
• A vacuum sealed glass container consists of Cathode, Anode and Grid.
Second
generation computers (1959-1964)
•
Transistors as the main electronic components.
• Magnetic
cores for internal memory and magnetic tapes and disks for external storage.
• Also used
punched cards and paper tape for external storage.
• Smaller,
more reliable, and more powerful than the first-generation computers.
• Consumed
less electricity and generated less heat than the first-generation computers.
• Punched
cards as an input device and printers as an output device.
• faster than
1st generation and could perform tasks in microseconds.
• Could be
programmed in assembly and high-level languages such as COBOL (Common
Business-Oriented Language), FORTRAN (Formula Translator), and ALGOL
(Algorithmic Language).
Transistor
(Transfer Resistance)
• A small
device invented by John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley at the
Bell Laboratories on December 23, 1947.
• Made up
of semiconductor materials like silicon and germanium.
• Used to
control the amount of current or voltage or used for amplification/modulation
or switching of an electronic signal.
• Smaller
than a vacuum tube and has a higher operating speed.
• Can do
the work of 1000 vacuum tubes.
Third
Generation Computers (1965-1974)
•
Integrated circuits as the main electronic components.
•
Semiconductor memory for the internal storage medium and magnetic tape,
magnetic disk (i.e., floppy disk, hard disk) for the secondary storage.
• Faster
than 2nd generation and could performed tasks in a nanosecond.
• Keyboards
as an input device and monitors as an output device.
• Operating
systems. & could run different programs.
• More
reliable and better in performance.
• Could be
programmed in high level languages like FORTAN, COBOL, PASCAL, C, C++, etc.
Integrated Circuit (IC)
• used in a
variety of devices, including microprocessors, audio and video equipment, and
automobiles.
• Developed
by Jack Kilby and Robert Noyce in 1958 AD.
• A miniaturized electronic circuit that contains several transistors and other electronic components like resistors, capacitors, etc. on a single wafer or silicon.
Fourth
Generation Computers (1975 And onwards)
• VLSIs
(microprocessor) and LSIs as the main electronic components.
• Magnetic
tape, magnetic disk, optical disk (CD/DVD/Blu-ray), flash memory and SSD for
external storage.
•
Semiconductor memories for internal memory.
• Advanced
input/output devices like mouse, touch screen, LCD, LED, Colour Printer, etc.
• Used
GUI-based operating system
•
Microcomputers (personal computers) are introduced.
• Laptop
and palmtop computers are also developed in this generation.
•
Processing speed is increased and measured in a picosecond.
• More
versatile, diligent, and reliable.
• They can
understand billions of instructions within a second.
• High
level languages (i.e., 4th generation languages).
Microprocessor
(VLSI)
• An
integrated circuit that consists of millions of transistors on a single silicon
chip.
• Executes
instructions and carries out arithmetic and logical operations.
• Can be of
4-bit, 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit, and 64-bit.
• The first
microprocessor, ‘Intel 4004’, which was developed by Marcian Ted Hoff of Intel
Corporation in 1971 AD, was a 4 bit and had 2300 transistors.
• The Core
2 Duo microprocessor contains more than 2.9 billion transistors on it.
• Speed of
a microprocessor is measured in clock speed i.e., Hertz (Hz).
5th
Generation Computer (Present and Beyond)
• Will be
based on ULSI technology.
• Will have
artificial intelligence and be able to think and understand human languages.
• Will have
a faster and larger primary memory.
• Will have
multiprocessors and parallel processing capacity.
• Will be
faster than their predecessors and the processing speed will be measured in
femtoseconds.
• Will have
larger primary and secondary storage as compared to their predecessors.
1.1.3
MEASURMENT UNIT OF PROCESSING SPEED AND STORAGE UNIT
• The processing speed of a computer is measured in
fractions of a second.
• The
processing speed of a computer can also be measured in hertz.
• The
storage capacity of a computer memory or storage device is measured in bytes or
higher units of bytes.
• The
storage capacity of a computer memory or storage device is measured in bytes or
higher units of bytes.
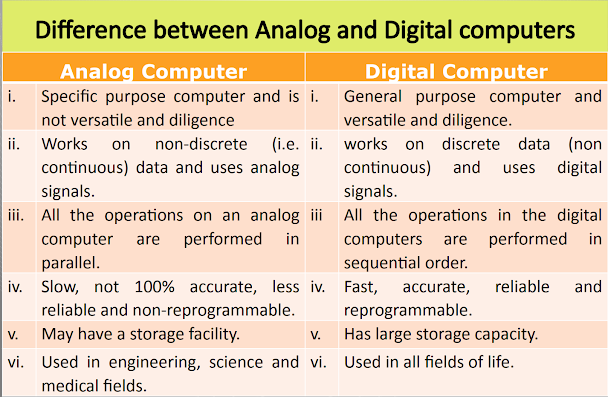
1.1.4 ANALOG,
DIGITAL and HYBRID COMPUTERS
• Analog
computer
– A special
purpose computer that can process only analog data (continuous varying physical
quantities like temperature, pressure, speed, depth, height, voltage, etc.).
– Cannot be
reprogram.
– Perform
operations in parallel.
• Digital computer
– Accept
discrete data (discontinuous data) like letters, numbers, symbols, figures,
etc. and process them.
– Perform
operations in sequential order.
– Can be
reprogrammed.
– Versatile
and diligence.
• Hybrid
Computer
– A special
purpose computer that has the capabilities of both digital and analog
computers.
– Can
convert analog data to digital data and vice versa.
– Used
mainly in specialized applications where both kinds of data (continuous and
discrete data) need to be processed.
1.1.5
MOBILE COMPUTING AND ITS APPLICATION
• A
technology that allows the transmission of data, voice and video through a
computer or any other wireless enabled device.
•
Application of mobile computing includes email, web browsing, messaging, e-commerce,
educational services, Emergency services, entertainment services and global position
system.
Features of
Mobile Computing device are:
·
It is a
portable device that can be used during mobility.
·
It has
limited processing and storage capability.
·
It includes
mobile communication, mobile hardware, and mobile software.
·
It usually
contains a touch screen for providing input. It contains an on-screen or
virtual keyboard for proving text inputs. However, an external keyboard can be
connected by using the USB port, infrared, or Bluetooth.
·
It contains
a camera, speaker, and microphone.
·
It contains
handwriting recognizing software.
·
Most of the
mobile computing devices contain a memory card slot to expand the storage
capacity.
·
It has
wireless connectivity such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi to connect the Internet or with
other computing devices as well as a wired connection through the USB port.
·
The most
mobile computing device can synchronize their data with applications on users'
computers.
·
It can be
used for cloud computing and remote access.
·
It uses a
mobile computing operating system such as Android, iOS, Windows Mobile OS, Palm
OS.
· It can include GPS (Global Positioning System) receiver for navigation.
Advantages
of Mobile Computing
·
It enables
users to work from any location at any time.
·
It saves
time for accessing data and information.
·
It helps to
increase the productivity of users reducing the time and cost.
·
It has made
research easier.
·
It is one
of the major handheld sources of entertainment of users at present.
·
Nowadays,
Business processes are easily available through secured mobile connections.
·
It is
portable.
·
It supports
cloud computing.
·
It provides
remote access to the organizational data from any location.
·
It is an
independent platform. It can be accessed from any hardware or software.
Disadvantages
of Mobile Technology
·
Mobile technology
requires faster and quality connectivity services that need either Wi-Fi or
GPRS or 3G or 4G connectivity.
·
It has
security concerns; most wireless connectivity is unsafe.
·
Large power
consumption due to the use of batteries continuously and they do not tend to
last long.
·
The danger
of misrepresentation i.e., credential verification is a problem.
·
Extensive
use of mobile devices results in health problems.
1.2
COMPUTER SYSTEM AND I/O DEVICES
• A
functional unit in which a group of integrated hardware works together with
software to fulfil the purposes of the instructions or programs.
• A
combination of different hardware and software that work together to process
data according to the instructions given by the user to give information.
• To
accomplish the basic operations, different hardware components like
input/output unit, CPU, and memory unit are involved in the computer system.
• These
different components of a computer are interconnected through buses which
transmit Data, instructions, and electric signals from one unit to another.
COMPUTER
ARCHITECTURE
• the
conceptual structural design and fundamental operational structure of a
computer system.
• the
conceptual design of different components of a computer system that defines how
the different components of the computer system are connected to each other.
• deals
with how to design a circuit for hardware components required for building a
computer and integrate those components to achieve functionality and
performance.
Computer
Organization
• the
components from which a computer is built.
• the
operational units and their interconnections that realize the architecture
specification.
• deals
with the physical components of a computer system that interact with each other
to perform various functionalities.
• deals
with physical aspects of computers like circuit designs, memory and its types, microprocessor
design, etc.
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF COMPUTER SYSTEM
COMPONENTS
OF COMPUTER SYSTEM
• Every
computer system has four basics components. They are:
a) Input
Unit
b)
Processing Unit
c) Output
Unit
d) Storage
Input Unit
• A device
or unit through which data and instructions are fed into the computer system.
• Accepts
or reads data and instructions from a user in human understandable form.
• Converts
these inputs in the computer acceptable form i.e., binary code.
• Transfers
the converted inputs into the computer system.
Processing
Unit
• Refers to
CPU, which is composed of ALU, CU and Registers/Memory Unit.
• ALU is
the part of the CPU where processing tasks (arithmetic and logical operations)
are performed.
• CU is the
part of the CPU that controls and directs all the components of the computer.
• A
resister is the part of CPU that stores data and instructions temporarily which
are currently being used in the computer.
Output Unit
• A device
or unit that displays or presents data, results of processing and other
information to the users in human understandable form.
• Accepts
the results of processing which is in binary coded form.
• Converts
binary coded form results into human understandable form.
• Presents
the converted results to the users.
Storage
Unit
• A
component of a computer that stores data, information, programs temporarily or
permanently.
• Primary
and Secondary memory are the two types of Storage.
• Primary
memory is the internal memory, which is accessible directly by the CPU and it
stores data and instructions input by a user, intermediate result of
processing, results of processing and currently running programs.
• Secondary
memory stores data and programs permanently and is not accessible directly by
the CPU.
Microprocessor
• Is an
integrated circuit that contains millions of transistors (i.e., electronic
components) packed onto a single chip.
• executes
instructions of a program, carries out arithmetic and logical operations, and
controls other components of a computer.
• is known
as the brain of the computer.
• The power
and performance of a microprocessor basically, depend on word length (address
bus), the number of transistors, and clock speed.
• More
number of transistors or electronic components on a microprocessor, more the
number of instructions sets.
• More the
instruction sets, more the commands or instructions that a microprocessor can
understand and work on.
• A word
length refers to the number of bits of data bus that can be moved between
storage and the processor.
• The word
length determines the number of bits processed in a single instruction. More
word length means a wider address and data bus and more amount of data
processed at a time.
• The clock
speed of a microprocessor refers to the capability of executing instructions per
second by a processor and is measured in megahertz (MHz).
Component
of Microprocessor
a. Bus
Interface Unit
b. Prefetch
Unit
c. Segment
and Paging Unit
d. Decode
Unit
e.
Execution Unit
f. Cache
memory (L1)
Bus
Interface Unit
• BIU is
the part of the microprocessor that links the CPU with the other components of
a computer.
• It
handles all the transfer of control signals, data and addresses on the buses
for the execution unit (EU).
• It sends
out addresses, fetches instructions from memory, reads data from ports and
memory, and writes data to ports and memory.
Execution
Unit
• EU
receives program instruction codes and data from the bus interface unit, executes
them, and stores the results in the general registers.
• It can
also store the data in a memory location or send it to an I/O device by passing
the data back to the BIU.
• it
receives and outputs all its data through BIU.
• It has
four subunits: arithmetic logic unit, registers, control unit, and protection test
unit.
• The ALU
performs arithmetic and logical operations on data.
• A
register holds instructions, storage addresses, and data that are currently
being used in a computer.
• The
control unit (CU) controls the flow of data through the processor and coordinates
the activities of the other units within it.
• The
Protection Test Unit acts as a traffic constable and verifies the address of
the data which is sent by the Control Unit from the Decode Unit. It makes sure
that every operation is done in the right way.
Prefetch
Unit
• decides
and instructs the BIU to retrieve data and instructions from the main memory
(RAM).
• queues
instructions to assure that the microprocessor is in continuous operation.
Segment and Paging Unit (memory management unit)
• converts
internal logic addresses into external memory addresses.
Decode Unit
• decodes
or translates instructions into a simple format understood by the ALU and
registers. It makes processing more efficient.
Function of
Microprocessor
•
Supervises and controls I/O devices.
• Transferring
data between memory and I/O devices
• Fetching
instructions from the main memory
• Decoding
instruction to determine what action is required to be done.
• Fetching
required data from the main memory or I/O devices based on fetched instruction.
•
Performing arithmetical and logical operations
•
Transferring the results of execution to memory or an output device
• Executing
programs stored in memory
•
Performing communication among the I/O devices etc.
1.2.4
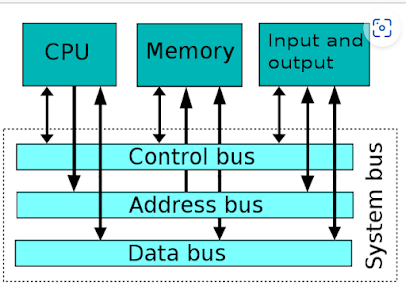
SYSTEM BUS
•It is an
electric pathway or communication path that interconnects different components
of a computer system and through which data, instructions, and electric signals
are transmitted from one device to another.
• is the
lining of wires through which bits are transmitted between the components of a
computer system.
• Can be 8-bit,
16-bit, 32-bit, or 64-bit.
• Data bus,
control bus and address bus are the types of system buses.
Data bus
·
It is the
pathway through which data is transferred from one component to another.
·
It is one
directional for I/O devices and bi-directional for memory and the CPU. allows
for transferring data from RAM to the CPU and vice versa in both directions.
·
Allows for
the transferring of data from input devices to the main memory and from the
main memory to output devices in only one direction.
·
The wider
data bus can transmit more data at a time.
·
It may be
serial or parallel and can be of 32 bits, 64 bits or even more bits.
·
The serial
data bus has one wire or path, and carries all the bits, one after the other.
·
The
parallel data bus has many wires or pathways through which data are transferred
simultaneously.
·
USB and
SATA are the common serial data buses.
Control bus
• It
carries the timing and control signals necessary to control and coordinate the
activities of the entire computer system.
• It is
bi-directional for the CPU and other components.
• It is
used by the CPU to control, manage, and communicate with different components
by transferring control signals (commands) to different components.
• It is
used by other devices to transfer the status signals back to the CPU.
• It
manages the information flow between components, indicating whether the
operation is a read or a write and ensuring that the operation occurs at the
right time.
Address bus
• It is the
pathway used to transfer the addresses of memory or I/O devices where the next instruction
to be executed or the next piece of data will be found.
• It
carries a memory address and determines the location in memory that the
processor will read data from or write data to.
• It is
unidirectional from the CPU to all other components.
• The
number of bits of address bus determines the maximum size of memory that the processor
can access. The address bus of 16 bits can transfer a maximum 16-bit address, which
means it can address 65,536 different memory locations.
1.2.5
PRIMARY MEMORY
• It is the
part of the computer that stores data, information, instructions, or programs
either temporarily or permanently.
• It is a
semiconductor based internal memory.
• ROM and
RAM are two types of primary memory.
• ROM, also
called CMOS, contains the BIOS program (i.e., firmware) which can only be read
by the CPU but cannot be erased or deleted.
ROM
• also
called CMOS, contains the BIOS program (i.e., firmware) which
can only be
read by the CPU but cannot be erased or deleted.
• PROM,
EPROM and EEPROM are three types of ROM.
• PROM
allows a programmer to write the program or data once on it.
• EPROM
allows a programmer to rewrite the data or program on it by erasing the
pervious contents.
• EEPROM
allows a programmer to erase and reprogram repeatedly under the software
control.
RAM
• is a
semiconductor memory which is made up of several small storage areas called
locations or cells.
• stores
data, instructions, or programs temporarily. It is volatile in nature.
• SRAM and
DRAM are two types of RAM.
• SRAM
stores a bit of data if the electricity is provided to it.
• The
contents of SRAM do not require refreshing periodically.
• DRAM
stores data, instructions, or programs temporarily if the electricity is
provided to it.
• It is
required to be refreshed or recharged at the interval of time.
CACHE
MEMORY
• It is a high-speed
memory that is built into a CPU or on a separate chip and is placed in between
the CPU and the main memory, whose access time is very close to the processing
speed of the CPU.
• The cache
built into the CPU is known as the Level 1 (L1) cache.
• The cache
built on a separate chip is known as the Level 2 (L2) cache.
• The Level
2 cache acts as a buffer between the CPU and the main memory.
• The OS
transfers data and program that are most frequently used by
the CPU to
cache memory where microprocessor first checks the required data and
instructions.
• It helps
to reduce data accessing time and improves overall system speed.
Buffer
•It is an
area of memory used for the temporary storage of data when a program or hardware
device needs an uninterrupted flow of information.
•It enables
the CPU to manipulate data before transferring it to a device.
•It helps
to run a computer efficiently.
•Buffers
are usually created in Random Access Memory (RAM) rather than other devices. Some
hardware devices like printer, hard disk come with their own on-board RAM.
•Printers
usually have smaller buffers which hold the data sent from the computer for printing
and make free system RAM to handle other tasks. This allows print jobs to run in
the background and is referred to as SPOOLING.
•Many
programs like word processor, use a buffer to keep track of changes to files
and updates the disk file with the contents of the buffer when the file is
saved.
•While
watching online videos, parts of the video files are download continuously and are
stored on the buffer before beginning to play which makes the smooth video playing.
Virtual
memory
•A computer
has limited amount of main memory (RAM), which is broken up into smaller
segments (i.e., pages).
•When many
programs are running at one time, there may not be sufficient spaces (pages) in
RAM to load a new program. So, the computer system uses some uses some spaces
on a hard disk as a virtual memory.
•The
computer system transfers data from RAM to virtual memory which are not
currently used by the programs and makes free spaces in the RAM.
•Virtual
memory is the temporary space on a hard disk which stores data of RAM which are
not currently used by the programs.
•When the
data in the virtual memory is required, the computer system moves other pages
to the virtual memory and brings the required pages back to RAM. This process
is known as paging or swapping and the temporary storage space on the hard disk
is called a page file or a swap file.
1.2.6
SECONDARY MEMORY
• A device
that stores data permanently.
• The CPU
cannot access the data and programs on a secondary memory, so data and programs
are required to transferred from it to RAM.
• Magnetic
disk, flash memory, optical disk, external storage device and memo stick are
the commonly used secondary memories.
Magnetic
Disk
• The most
popular direct access storage device that consists of a circular disc made of
metal or plastic and is coated with magnetic material.
• The
surface of a disk is divided into concentric circles called tracks and pie shaped
blocks called sectors.
• The data
is stored on the tracks of a disk surface in the form of invisible tiny
magnetic spots. A positive magnetized spot represents a 1 bit, and the negative
magnetized spot represents a 0 bit.
• Magnetic
disks are reliable and durable storage devices. Hard disk, floppy disk, zip
disk, super disk, Jaz disk, etc. are the magnetic disks.
• A hard
disk is the most used secondary storage device that consists of one or more
metal disks (called platters) coated with magnetic material where data are
stored. The read/write head reads and write data. on the platters.
• Other
magnetic disks except hard disk are not used nowadays.
Flash Memory
• is an
electrically erasable programmable read-only memory (EEPROM).
• It is
available as a USB memory stick (pen drive) and solid-state drive (SSD).
• When a
pen drive is plugged into a computer's USB port, it behaves like an external
disk drive. A pen drive is specially used for transferring data, songs, games,
and programs from one computer to another.
• A solid-state
drive (SSD) uses flash memory chips to store data and is comparatively faster
and more reliable than a hard disk.
• SSD has mainly two components: a flash
controller and NAND flash memory chips.
Optical
Disk
•A storage
device that uses laser light technology to store and retrieve data.
•An optical
disc is a circular disk made of rigid plastic or metal that is coated with highly
reflecting material.
•While
writing data, a high intensity laser beam is focused on the metal coated surface
of the optical disk which forms tiny holes (or pits) on the metal coated surface
of the disk along its tracks. A pit represents a value of 1 and a flat spot or land
represents a value of 0.
•While
reading, a low intensity laser beam is focused on the disk surface and the reflected
laser is sensed by a photodiode (light sensitive semiconductor diode). The intensity
of reflected laser beam from the pits is weak and is high from the flat spots.
These high and low patterns of the reflected laser beam are sensed by photodiode
and converted into electronic signals.
•The
commonly used optical disks are Compact disk, Digital versatile disk, and
Blu-ray disk. A CD can store 600-700 MB data. A DVD can store 4.7 GB to 17 GB
data. A BD can store 25 GB to 100 GB data.
•A computer
system needs optical disk drive to access the contents of an optical disk.
1.2.7 INPUT
DEVICES
• A device
through which data and instructions are entered into the computer system.
• converts
the human understandable data and instructions into electronic signals that a
computer understands and transfers to RAM.
• The data
or instructions that are entered into a computer are known as input.
• Keyboard,
mouse, scanner, light pen, optical magnetic reader (OMR), optical character
reader (OCR), Bar code reader (BCR), magnetic ink character recognition (MICR),
touch pad, Touch Screen, microphone, digital camera, joystick, etc., are input devices.
a. Keyboard
– An input
device that contains alphabet keys, number keys, punctuation mark keys and some
other characters keys.
– used for
entering data like letters, text, numbers, symbols, and instructions to a
computer.
– When a
key is pressed, the keyboard encoder (electronic circuit) recognizes the
pressed key and generates the related binary code and transmits it to the
computer. For example, when you press an alphabet key ‘A’, a keyboard encoder
generates binary code ‘01000001’.
b. Mouse
– A small
handheld input device that allows a user to point and select items, icons or
commands displayed on the graphical user interface (GUI) environment.
– consists
of a plastic housing or casing with a flat bottom and two or three buttons on
the top surface.
– A mouse
may be a mechanical mouse or optical mouse.
c. Touch
Pad
– A
touch-sensitive pad which works like a mouse and is used on a laptop.
d. Light
Pen
– A
pen-shaped input device that has light-sensitive element on the tip of it and
when it is placed
against the
screen, it detects the light from the screen, enabling the computer to identify
the location of the pen on the screen.
– It is
used to draw pictures or select menu options onto the screen by directly
pointing at the menus.
e. Scanner
– An input
device that makes duplicate of any photo, handwritten or printed document in
digital form into a computer.
– It works
like a photocopy machine.
– Flat-bed
scanners and handheld scanners are the most used scanners.
– A flatbed
scanner has a sheet of glass over which a photo or printed text to be scanned
is placed.
– A
handheld scanner is a portable scanner that can be held in a user's hand and
moved over the document to be scanned.
f. Optical
Mark Reader (OMR)
– An input
device that uses a light source to read marks and converts them into digital
data that a
computer
can process.
– It can
read and count a pre-specified type of mark, such as small circles or
rectangles made with a pencil or ball pen.
g. Optical
Character Reader (OCR)
• An input
device that uses a light source to read characters and converts them into
digital data that a computer can process.
h. Magnetic
Ink Character Reader (MICR)
• used in a
bank to process a large volume of cheques and demand draffs.
• When a cheque
is brought by a person to cash, the cheque is kept in the MICR, which reads the
data and transfers the information to the CPU for immediate processing.
i. Bar Code
Reader
• An input
device that reads the Universal Product Code (UPC) of a bar code and transfers
it to a computer.
• A bar
code represents data in a set of vertical parallel lines of varying thicknesses
with gaps.
• Books and
goods in the market are labelled with bar codes.
j. Touch
Screen
• A
touch-sensitive electronic visual display screen which enables a user to input
data or instructions just by selecting items displayed on a screen by using a
stylus or finger.
• Touch
screens are common in devices such as laptops, mobile phones, tablets, electronic
voting machines, point of sale (POS) systems, ATMs, interactive multimedia boards,
car GPS, kiosks, and token dispensers. Laptop with Touchscreen Laptop with
Touchscreen Interactive Board Interactive Board
k. Digital
Camera
– An input
device which captures pictures and videos and stores them in a digital format
in the memory chip.
– The
photos stored in the digital camera can be viewed and erased immediately.
l.
Microphone
– An input
device used for entering audio, sound, or voice into a computer.
– It
captures sound waves, converts them into digital format, and provides them to
the CPU.
– The input
sound or voice can be saved on a computer as a sound file.
1.2.8
OUTPUT DEVICES
• All the
devices that are used to display or present the result of processing and other
information to the user in a human understandable form are known as output
devices.
• Monitor,
printer, speaker, projector, and plotter are output devices.
• Output
devices may be softcopy output devices or hardcopy output devices.
• The
output displayed or presented by a softcopy output device is not permanent. A
monitor, speaker, and projector are softcopy output devices.
• The
output displayed or presented by a hardcopy output device is permanent. A
printer and a plotter are the hardcopy output devices.
a. Monitor
• Also
known as a visual/video display unit (VDU) or video display terminal (VDT).
• It displays
data, information, or the result of processing on its screen.
• Softcopy
output device.
• Monitors
may be CRT monitor or LCD/LED monitor.
• A CRT
monitor is based on a cathode ray tube.
• Both LCD
and LED monitors use liquid crystal to form images.
•
Fluorescent lamps or tubes that are used as the backlight in LCD monitor.
•
Light-emitting diodes are used as the backlight in a LED monitor.
b. Speaker
• A
softcopy output device that plays sound generated by the computer.
• A speaker
is needed to connect to the soundcard of the computer.
c. Printer
• A
hardcopy output device that displays the data or result of processing on paper.
• Printers
may be non-impact printers or impact printers.
1.2.9 HARDWARE INTERFACES
a. Serial
Port
·
A 9-pin
serial communication interface port through which 1 bit of data can be
transferred.
· commonly used to connect a mouse and modem.
b. Parallel
port
• A 25-pin
connector/interface that connects an external device, such as printer, scanner,
or Zip disk drive.
•
Centronics port.
• It can
transfer 8 bits of data simultaneously.
c.
Universal serial bus (USB) Port
·
the most
used interface in the computer system nowadays for connecting peripheral
devices like keyboard, mouse, digital camera, printer, scanner, etc.
·
It can
support a maximum of 127 external devices at a time on a computer.
d. Firewire
·
A high-speed
serial bus for connecting high speed devices like audio/video equipment, aeronautical
devices, medical equipment, etc.
·
It can
transfer 400 MB of data per second.
·
It can
support up to 63 external devices at a time on a single computer.
e. High-definition multimedia interface (HDMI) Port
·
A port used
for connecting audio/video equipment.
·
A monitor,
projector, digital camera, etc. can be connected through the HDMI ports.
f. Expansion Slots
·
A socket on
the motherboard that allows an expansion card/daughter board to be connected.
·
A computer
motherboard may have PCI Express, PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect), AGP (Accelerated
Graphics Port) or ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) slots.


































Comments
Post a Comment